
Meteorological Instruments Aid in Accurate Weather Forecasting and Disaster Prevention
This article explores the importance of meteorological instruments in weather forecasting and their role in disaster prevention and mitigation.

This article explores the importance of meteorological instruments in weather forecasting and their role in disaster prevention and mitigation.
In today's world, weather forecasting and disaster prevention are critical for protecting lives and property. These two areas depend heavily on meteorological instruments, which provide accurate data and insights into the weather patterns and changes. With the advancement of technology, meteorological instruments have become more sophisticated and reliable, making them indispensable tools for meteorologists and emergency management officials. This article explores the importance of meteorological instruments in weather forecasting and their role in disaster prevention and mitigation.
Meteorological instruments are devices used to measure various meteorological parameters, such as temperature, pressure, humidity, wind speed and direction, rainfall, and solar radiation. These instruments collect data, which is then used to make weather predictions and to monitor the weather patterns over time. The use of meteorological instruments dates back to the early 17th century when the first weather instrument, the thermometer, was invented.
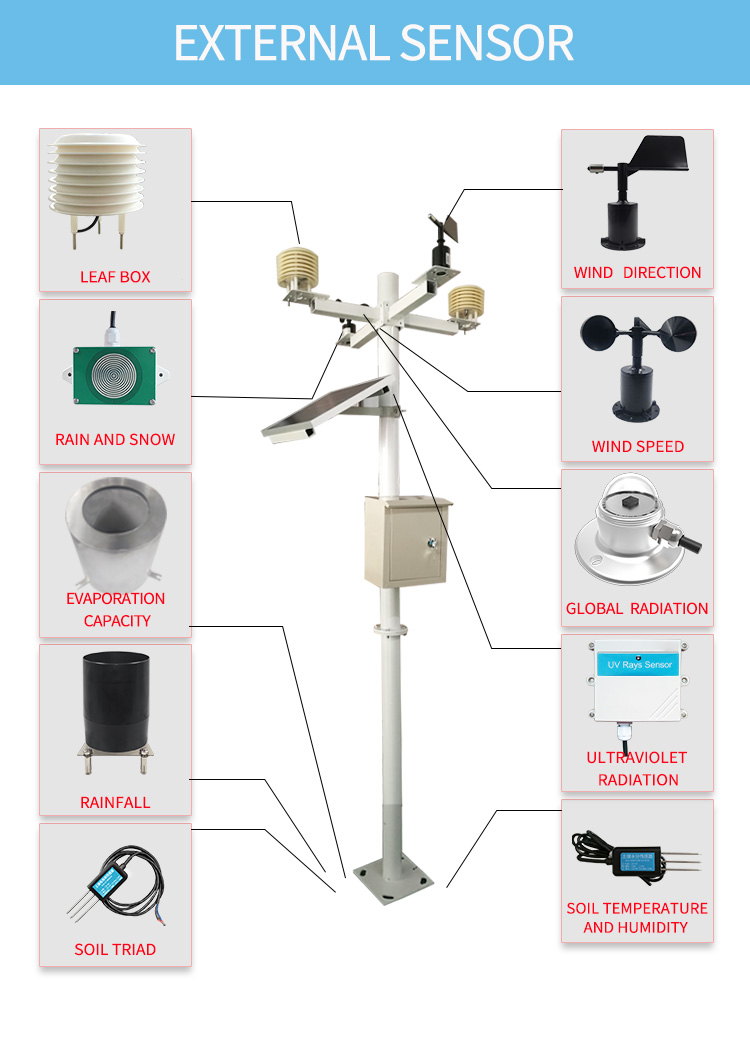
Weather forecasting is the process of predicting the weather conditions for a specific location over a period. Weather forecasts are essential for various sectors, including aviation, agriculture, tourism, and disaster management. Meteorological instruments play a crucial role in weather forecasting, as they provide the data needed to make accurate predictions.
Temperature Measurement
One of the most important meteorological instruments used in weather forecasting is the thermometer. Thermometers measure the temperature of the air, which is an essential parameter for weather forecasting. Temperature data is used to predict weather patterns such as cold fronts, warm fronts, and temperature inversions. These patterns help meteorologists predict the likelihood of rain, snow, or storms.
Barometric Pressure Measurement
Barometric pressure is another critical parameter in weather forecasting. It is measured using a barometer, which determines the pressure exerted by the atmosphere. Changes in barometric pressure can indicate a change in weather patterns. For instance, a falling barometer reading can indicate an approaching storm.
Humidity Measurement
Humidity is the amount of moisture in the air. It is measured using a hygrometer. Humidity data is important in predicting the likelihood of precipitation, as moisture is a crucial ingredient for rain and snow.
Wind Speed and Direction Measurement
Wind speed and direction are measured using an anemometer and a wind vane, respectively. Wind data is critical in predicting the intensity and direction of storms, as well as the likelihood of tornadoes and hurricanes.
Rainfall Measurement
Rainfall is measured using a rain gauge, which collects and measures the amount of precipitation over a specific area. Rainfall data is used to determine the total precipitation over time, as well as to predict the likelihood of flooding and drought.

Disasters can cause significant damage to property and loss of life. To minimize the impact of disasters, meteorological instruments play a crucial role in disaster prevention and mitigation.
Meteorological instruments are used to create early warning systems for disasters such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and floods. Data collected by these instruments is analyzed to create models that predict the likelihood and severity of disasters. This information is then used to issue warnings to the public, giving them time to prepare or evacuate.
Floods are one of the most devastating disasters, causing significant damage to property and loss of life. Meteorological instruments, such as rain gauges and river gauges, are used to monitor the water levels of rivers and streams. This data is used to create flood maps and models, which help emergency management officials identify areas that are at risk of flooding.