Farming is one of the oldest industries in the world, but it's also one of the most challenging. Every year, growers face more pressure to produce higher yields while using fewer resources. At the same time, they must minimize their impact on the environment, protecting soil health and water supplies. Farmers around the world are increasingly turning to technology – specifically, soil sensors – to help tackle this complex challenge.
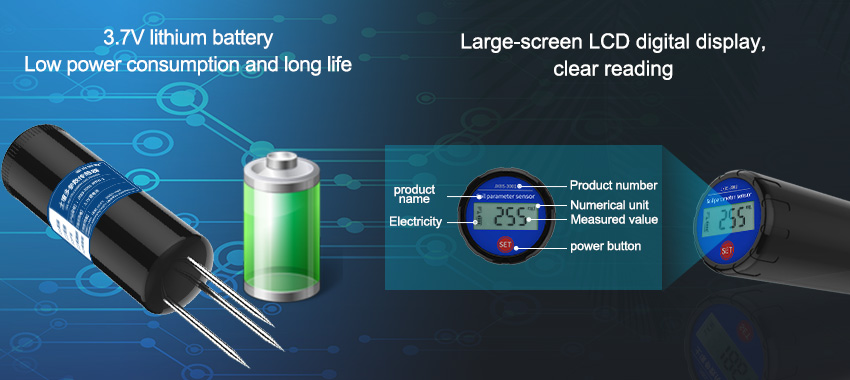
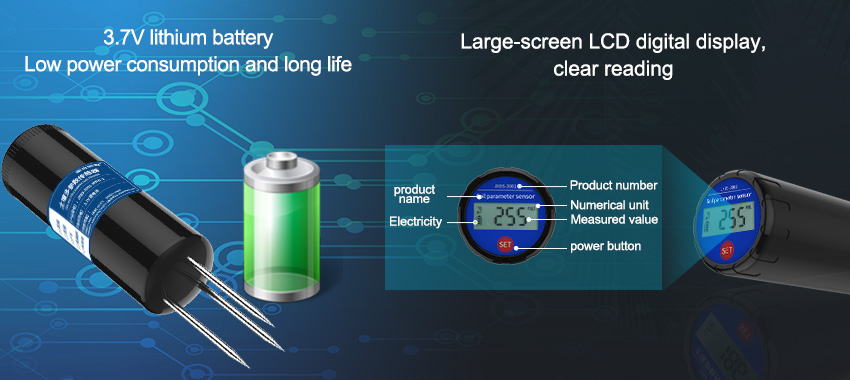
Soil sensors are small devices placed in the soil to monitor various conditions such as temperature, moisture, pH levels, nutrient content, compaction levels, and more. Once installed, these sensors collect and transmit data to a central database or cloud-based platform, where it can be analyzed by growers and agronomists alike. With this information at their fingertips, farmers can make more informed decisions about how to grow their crops.
One of the primary ways soil sensors are transforming farming is by enabling precision agriculture. In the past, growers applied fertilizers, herbicides, and pesticides uniformly across entire fields, often wasting resources and risking crop damage. Today, however, soil sensors allow farmers to tailor applications precisely to each square foot of soil, helping to optimize inputs and reduce waste. By pinpointing areas that require the most attention, growers can adjust the amount and timing of inputs to maximize yield and minimize environmental impact.
By constantly monitoring soil conditions, soil sensors also help growers detect early signs of plant stress and disease. This enables them to take action before an issue can become significant, increasing the chances of successfully solving it. For example, if soil sensors detect a sudden change in moisture levels over the course of several days, growers can be alerted that a pivot irrigation system may have malfunctioned. Additionally, color changes in plants can indicate nutrient deficiencies like nitrogen or iron; with soil sensors to help manage plant fertility, treatment starts quickly, saving resources and maintaining productivity.
Soil sensors are an essential ingredient in overcoming challenges like water availability, nutrient depletion, and soil compaction. By providing real-time information about soil moisture levels, farmers can manage irrigation schedules more effectively – leading to less crop stress and water waste. Sensors for nutrient monitoring allow precise application of nitrogen and other fertilizers to plant roots, improving the energy efficiency utilized while also decreasing environmental impacts.
While soil sensors' cost presents arguably the most significant hurdle for their widespread adoption, economies are affected positively by incorporating technology into agriculture processes. Soil sensors technology enables better decision-making and save workers hauling lab equipment out to fields and back. Manually collecting soil samples is expensive and time-consuming, with results often arriving too late to be useful. In contrast, wireless soil sensor systems provide 24/7 data collection and real-time adjustments of input volumes that translate into savings, timely crop growth observations, and reduced environmental degradation.
Finally, the rise of Big Data has made it easier than ever to gain a broad perspective on how farming practices impact the land around us. Previously, difficult manual analysis that was subject to errors was necessary to ensure healthy crops. With today's cloud-based databases and machine learning algorithms built-in soil sensors, Big Data analysis becomes manageable.