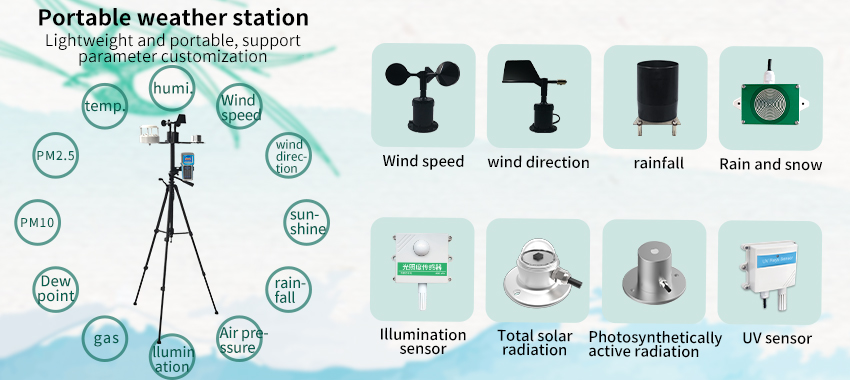
Accurate weather monitoring is essential for various industries, including agriculture, aviation, transportation, and disaster management. Weather stations play a crucial role in collecting and analyzing meteorological data to provide precise and real-time weather information. In this article, we will explore the importance of utilizing weather stations for weather monitoring and analysis, their components, and the benefits they bring in terms of predicting weather patterns, enhancing safety measures, and optimizing resource management.
Understanding Weather Stations: Weather stations are automated systems that consist of various instruments and sensors designed to measure and record weather parameters. These stations are strategically located at different geographic locations to ensure comprehensive coverage. The primary components of a weather station include:
a. Thermometer: Measures air temperature.
b. Hygrometer: Measures relative humidity.
c. Barometer: Records atmospheric pressure.
d. Anemometer: Gauges wind speed and direction.
e. Rain Gauge: Collects and measures precipitation.
f. Pyranometer: Measures solar radiation.
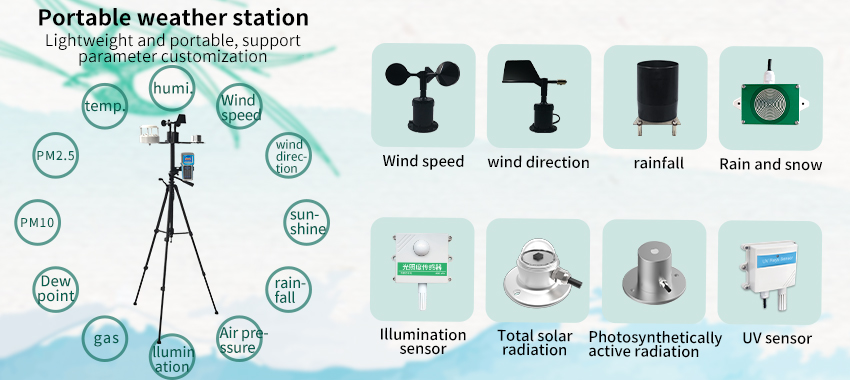
Importance of Weather Monitoring and Analysis: a. Agricultural Sector: Accurate weather data is vital for farmers to make informed decisions about crop selection, planting schedules, irrigation, and pest control. By analyzing weather patterns, farmers can optimize resource allocation, maximize crop yields, and minimize losses caused by adverse weather conditions.
b. Aviation and Transportation: Weather stations provide critical information for aviation safety and air traffic control. Pilots rely on weather updates to plan flight routes, avoid turbulence, and anticipate any severe weather conditions that may affect flight operations. Similarly, the transportation sector utilizes weather data to optimize travel routes, mitigate potential road hazards, and minimize delays caused by adverse weather conditions.
c. Disaster Management: Precise weather monitoring and analysis assist in predicting and preparing for natural disasters such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and floods. By analyzing weather patterns, authorities can issue timely warnings, evacuate vulnerable areas, and allocate resources for disaster response.
d. Energy Generation: Weather stations play a significant role in optimizing energy generation from renewable sources such as solar and wind power. By analyzing solar radiation and wind patterns, energy companies can predict energy production levels, plan maintenance schedules, and ensure efficient utilization of available resources.
Benefits of Utilizing Weather Stations: a. Accurate Weather Forecasting: Weather stations collect real-time data that is essential for accurate weather forecasting. Advanced analytical tools and models can process this data to predict short-term and long-term weather patterns. Accurate forecasting helps individuals and organizations make informed decisions, whether it's planning outdoor activities, managing agricultural practices, or implementing safety measures.
b. Safety Measures: Weather stations provide valuable information for the implementation of safety measures in various industries. For example, in aviation, pilots rely on weather updates to avoid turbulent areas and ensure passenger safety. Similarly, transportation authorities utilize weather data to manage road conditions, minimize accidents, and ensure safe travel.
c. Resource Optimization: By utilizing weather station data, organizations can optimize resource management. For instance, in agriculture, farmers can efficiently allocate water resources by aligning irrigation schedules with rainfall patterns. This minimizes water waste, reduces costs, and promotes sustainable farming practices. Similarly, energy companies can optimize energy generation by analyzing weather patterns, leading to more efficient utilization of resources.
d. Climate Change Research: Weather station data plays a critical role in climate change research. Long-term weather records obtained from weather stations help scientists study historical weather patterns and assess climate changes over time. This data aids in understanding the impacts of climate change and formulating strategies to mitigate its effects.
Technological Advancements in Weather Stations: Weather station technology has seen significant advancements in recent years. Some notable developments include:
a. Remote Sensing: Weather stations equipped with remote sensing capabilities, such as satellites and radar systems, can provide a broader and more comprehensive view of weather conditions. These remote sensing technologies enable meteorologists to monitor weather patterns over large geographic areas, enhancing the accuracy of weather forecasts.