Water is a vital resource for sustaining life on Earth, and the health of our aquatic environments is crucial for the well-being of both human and animal populations. However, with increasing human activities and industrialization, our water bodies are facing unprecedented levels of pollution and degradation. To effectively address this issue, water quality monitoring plays a pivotal role in detecting pollution and protecting our precious aquatic ecosystems. In this article, we will explore the importance of water quality monitoring, its methods, and how it contributes to the preservation of our aquatic environments.
Understanding Water Quality Monitoring:

Water quality monitoring refers to the systematic process of assessing the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water bodies to determine their overall health and identify potential sources of pollution. This involves regular sampling, analysis, and interpretation of various parameters including temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, turbidity, nutrient levels, toxic substances, and microbial indicators. By monitoring these parameters, scientists and environmental agencies can gauge the overall quality of water bodies and assess any changes or trends over time.
The Importance of Water Quality Monitoring:
Early Detection of Pollution:
Water quality monitoring allows us to detect and identify pollutants at an early stage. By regularly monitoring key parameters, authorities can identify changes in water quality that may be caused by human activities such as industrial effluents or agricultural runoff. Early detection enables quick response measures to mitigate pollution sources before they cause significant harm to aquatic ecosystems and human health.
Protection of Aquatic Ecosystems:
Aquatic ecosystems are homes to diverse species of plants and animals, many of which are highly sensitive to changes in water quality. Monitoring water quality helps in understanding the impact of pollution on these ecosystems, enabling us to take necessary conservation measures. By regularly monitoring parameters like dissolved oxygen levels, nutrient concentrations, and toxicity levels, scientists can assess the ecological health of water bodies and implement strategies for habitat restoration, species protection, and biodiversity conservation.
Preservation of Human Health:
Safe drinking water is essential for human health and well-being. Water quality monitoring is crucial for ensuring the safety of our water sources by identifying potential contaminants. Regular testing allows authorities to detect harmful bacteria, viruses, heavy metals, and other pollutants that may pose risks to human health. By understanding the quality of our water resources and implementing appropriate treatment measures, we can prevent waterborne diseases and safeguard public health.
Support for Policy and Regulation:
Water quality monitoring provides valuable data and information that support the development of policies and regulations for the preservation and management of water resources. Monitoring allows policymakers to assess the effectiveness of existing regulations and make informed decisions regarding pollution control measures. Furthermore, monitoring data can be used to educate the public, raise awareness about water quality issues, and promote sustainable practices in water use and conservation.
Methods of Water Quality Monitoring:
Field Monitoring:
Field monitoring involves collecting water samples directly from the source for immediate analysis. This method often utilizes portable instruments to measure parameters such as temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, and conductivity on-site. Field monitoring provides real-time data, allowing for immediate assessment of water quality and timely decision-making.
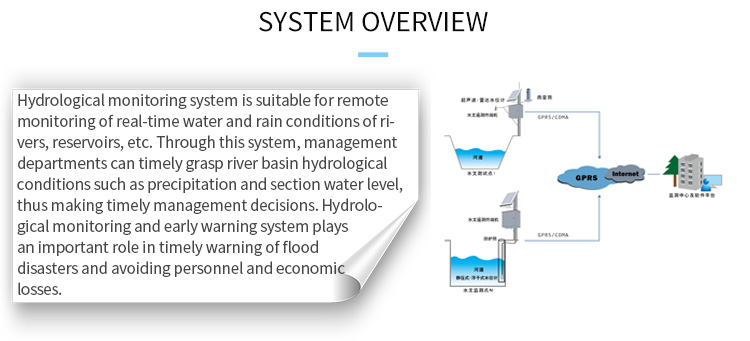
Laboratory Analysis:
Water samples collected through field monitoring or remote sampling are subjected to laboratory analysis to assess a wider range of parameters. Laboratory analysis provides more detailed and accurate measurements of various water quality indicators, including nutrient levels, pollutant concentrations, and microbial content. Advanced analytical techniques and instruments enable scientists to detect even trace amounts of pollutants, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of water quality.
Remote Sensing:
Remote sensing technologies, such as satellite imagery and aerial surveys, play a significant role in large-scale water quality monitoring. These techniques allow for the assessment of water quality over large areas, detecting changes in water surface temperature, algal blooms, sedimentation patterns, and other indicators of pollution. Remote sensing provides valuable data for long-term monitoring, trend analysis, and the identification of potential pollution hotspots.







