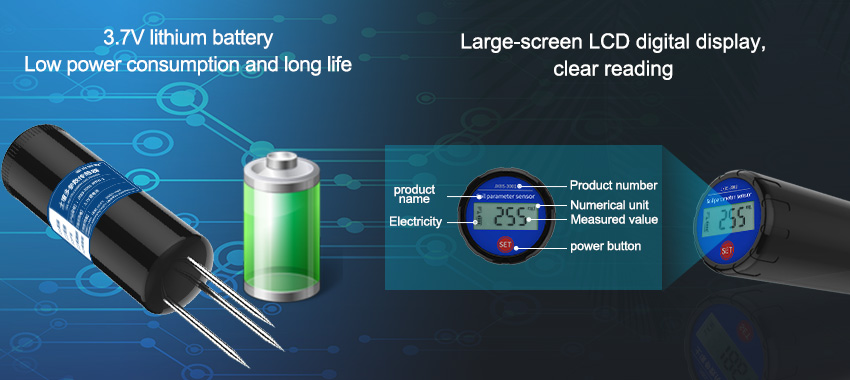
In the realm of modern agriculture, precision is key. The ability to optimize resource allocation and maximize crop yield is crucial for sustainable food production. One significant factor in achieving agricultural precision is understanding soil moisture levels. Soil moisture sensors have emerged as powerful tools that enable farmers to access real-time data on soil conditions, leading to enhanced irrigation management and improved overall productivity. In this article, we will explore the importance of soil moisture sensors in precision agriculture and how they can revolutionize farming practices.

The Significance of Soil Moisture:
Water is an essential resource for plant growth and development. However, lack of water or excessive irrigation can have detrimental effects on crops. Understanding the moisture levels in the soil is imperative for efficient water management. Traditional irrigation methods often rely on guesswork or fixed schedules, which can lead to under- or over-irrigation. Soil moisture sensors offer a solution by providing accurate and timely information on soil moisture content, empowering farmers to make informed decisions regarding irrigation.
Working Principle of Soil Moisture Sensors:
Soil moisture sensors operate based on various principles, including capacitance, tensiometry, and time domain reflectometry (TDR). Capacitance-based sensors measure the dielectric properties of the soil, which are directly related to soil moisture content. Tensiometric sensors rely on the measurement of soil tension, representing the force required to extract water from the soil. TDR sensors use electromagnetic waves to determine soil moisture levels based on the travel time of the waves through the soil. Regardless of the underlying principle, soil moisture sensors provide valuable data that can guide irrigation practices.
Benefits of Soil Moisture Sensors:
a. Precise Irrigation Management: By utilizing soil moisture sensors, farmers gain insights into the actual water needs of their crops. This information allows them to adjust irrigation schedules and quantities accordingly, leading to significant water savings and reduced environmental impact. Precise irrigation management ensures that plants receive the optimal amount of water at the right time, promoting healthy growth and maximizing crop yields.
b. Real-Time Data and Automation: Soil moisture sensors provide real-time data on soil moisture levels, allowing farmers to monitor changes and adjust irrigation settings promptly. Some advanced sensor systems are equipped with automation features, which enable automatic irrigation control based on preset thresholds. This automation reduces human error and ensures consistent and efficient irrigation practices.
c. Resource Optimization: Irrigation accounts for a significant portion of water usage in agriculture. By utilizing soil moisture sensors, farmers can optimize water consumption by only irrigating when necessary. This not only conserves valuable water resources but also reduces energy and labor costs associated with unnecessary irrigation practices.
d. Disease Prevention: Excessive moisture levels in the soil can contribute to the development of plant diseases, such as root rot or fungal infections. Soil moisture sensors help prevent these issues by alerting farmers to potential oversaturation in the soil. By avoiding over-irrigation, farmers can maintain optimal soil conditions and reduce the risk of disease outbreaks, resulting in healthier crops.
e. Enhanced Crop Quality: Proper moisture management is crucial for ensuring high-quality crops. By continuously monitoring soil moisture levels, farmers can provide the ideal growing environment for their plants. This leads to improved nutrient uptake, reduced stress on the plants, and ultimately, better-quality produce.
Integration with Data Analytics:
Soil moisture sensors generate a vast amount of data that, when combined with advanced analytics, can yield valuable insights for farmers. Data analytics platforms can analyze historical and real-time sensor data, identify patterns, and provide recommendations for optimizing irrigation strategies. These platforms can take into account factors such as weather forecasts, crop type, and soil characteristics to generate personalized irrigation plans. By harnessing the power of data analytics, farmers can further enhance their precision agriculture practices and maximize their crop yield potential.
Case Studies:
a. Vineyard Management: In the wine industry, soil moisture sensors have become an indispensable tool for vineyard management. Growers can monitor the moisture levels in the soil at different depths, enabling them to make informed decisions about irrigation. By adjusting water application based on sensor data, vineyard owners have experienced improved grape quality, reduced water usage, and increased efficiency in their operations.
b. Precision Farming in Corn Fields: Soil moisture sensors h