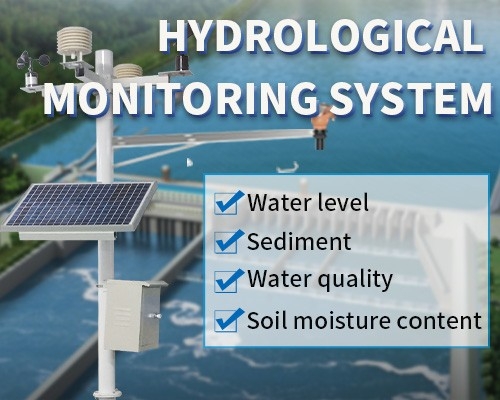
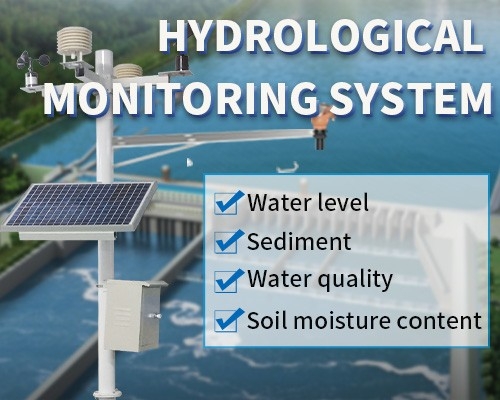
An Insight into Cutting-Edge Monitoring Equipment
These cutting-edge devices not only enhance operational efficiency but also play a crucial role in ensuring safety, preventing disasters, and facilitating data-driven

These cutting-edge devices not only enhance operational efficiency but also play a crucial role in ensuring safety, preventing disasters, and facilitating data-driven
In the rapidly evolving technological landscape, monitoring equipment has become indispensable across various industries, from healthcare to environmental science, from manufacturing to smart cities. These cutting-edge devices not only enhance operational efficiency but also play a crucial role in ensuring safety, preventing disasters, and facilitating data-driven
decision-making. This article delves into the intricacies of modern monitoring equipment, exploring its advancements, applications, and the transformative impact it is having on our world.
The journey of monitoring technology began with basic tools like thermometers, barometers, and seismometers, which were used for weather forecasting and geological studies. Over time, as electronics and digital technology advanced, so did the sophistication of monitoring devices. The advent of sensors, microcontrollers, and data communication technologies marked a significant leap, enabling real-time monitoring and remote access to critical information.
Today, cutting-edge monitoring equipment leverages artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing to provide unprecedented levels of accuracy, reliability, and connectivity. These technologies have revolutionized how we collect, analyze, and respond to data, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in various sectors.
Environmental monitoring is crucial for understanding climate patterns, protecting biodiversity, and ensuring sustainable development. Modern environmental monitoring systems employ a range of sensors to measure parameters such as temperature, humidity, air quality, soil moisture, and noise levels.
Air Quality Monitors: These devices use sensors to detect pollutants like PM2.5, PM10, NO2, SO2, CO, and O3. Advanced models integrate AI algorithms to predict air quality trends and issue alerts for potential health hazards.
Weather Stations: Equipped with anemometers, hygrometers, barometers, and rain gauges, weather stations provide comprehensive weather data. IoT-enabled stations can transmit this data in real-time, enabling accurate weather forecasting and disaster preparedness.
Smart Soil Sensors: These sensors measure soil moisture, pH levels, and nutrient content, helping farmers optimize irrigation and fertilization practices. They also facilitate precision agriculture, enhancing crop yields and reducing environmental impact.
The healthcare industry has seen tremendous advancements in monitoring technology, particularly in the realm of remote patient monitoring (RPM). Wearable devices, implantable sensors, and telemedicine platforms have transformed healthcare delivery.
Wearable Health Monitors: Devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers monitor heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, sleep patterns, and physical activity. They can alert users to potential health issues and provide data for diagnostic purposes.
Implantable Sensors: These tiny devices are surgically inserted into the body to monitor vital signs continuously. They are particularly useful in managing chronic conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and epilepsy.
Telemedicine Platforms: These platforms facilitate remote consultations, allowing patients to connect with healthcare providers via video calls. Integrated with monitoring devices, they enable real-time health assessments and timely interventions.
In the industrial sector, monitoring equipment is essential for ensuring operational safety, optimizing production processes, and preventing downtime.
Machine Health Monitors: Vibration sensors, thermographic cameras, and acoustic emission detectors are used to monitor the health of industrial machinery. AI algorithms analyze this data to predict maintenance needs, reducing unexpected failures and extending equipment lifespan.
Process Monitoring Systems: These systems monitor various parameters in manufacturing processes, such as temperature, pressure, flow rates, and chemical compositions. They ensure product quality, enhance process efficiency, and comply with regulatory standards.
Occupational Health and Safety Monitors: Industrial environments often require monitoring of hazardous substances, noise levels, and ergonomic factors. Modern monitoring solutions provide real-time data and alerts, helping to prevent occupational illnesses and injuries.
Smart cities leverage cutting-edge monitoring technology to enhance urban living, improve public safety, and optimize resource use.
Traffic Management Systems: These systems use cameras, sensors, and AI to monitor traffic flow, detect accidents, and manage traffic signals. They reduce congestion, improve road safety, and enhance emergency response times.
Structural Health Monitors: Sensors embedded in bridges, buildings, and other infrastructure monitor structural integrity. They detect cracks, movements, and vibrations, enabling proactive maintenance and preventing catastrophic failures.
Smart Energy Grids: Advanced meters, sensors, and analytics tools monitor energy consumption and distribution. They optimize energy use, reduce waste, and facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources.
The integration of AI and IoT is a cornerstone of modern monitoring technology. IoT enables devices to connect and communicate with each other, creating a vast network of interconnected sensors and systems. AI, on the other hand, provides the intelligence to analyze this data, identify patterns, and make predictive insights.
Real-Time Data Analysis: IoT devices transmit data in real-time, allowing for immediate insights and prompt responses. AI algorithms process this data at unprecedented speeds, enabling quick decision-making.
Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing historical data and current trends, AI can predict when equipment will fail, enabling proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
Enhanced Accuracy and Reliability: AI-powered algorithms improve the accuracy of measurements and reduce false positives and negatives. This enhances the reliability of monitoring systems and reduces the need for manual intervention.
Scalability and Flexibility: IoT-enabled monitoring solutions are scalable, allowing for easy expansion as needs grow. AI provides the flexibility to adapt to new data sources and changing requirements.
Despite the significant advancements in monitoring technology, several challenges remain. Data privacy and security are paramount concerns, especially as more devices connect to the internet. Ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information is crucial.
Moreover, interoperability between different monitoring systems and platforms is a challenge. Standardization efforts are needed to facilitate seamless data exchange and integration.
The future of monitoring equipment lies in continuous innovation and integration of emerging technologies. Quantum computing, for instance, has the potential to revolutionize data processing capabilities, enabling even more complex and accurate analyses.
Additionally, the development of more sustainable and eco-friendly monitoring solutions is essential. This includes reducing the energy consumption of devices and using recyclable materials in their manufacture.
Cutting-edge monitoring equipment is a testament to the rapid pace of technological advancement. From environmental monitoring to healthcare, from industrial applications to smart cities, these devices are transforming how we collect, analyze, and respond to data. The integration of AI and IoT has significantly enhanced their capabilities, making them more accurate, reliable, and scalable.
As we move forward, addressing the challenges of data privacy, interoperability, and sustainability will be crucial. Continuous innovation and the adoption of emerging technologies will drive the next wave of advancements, further expanding the potential of monitoring equipment to improve our lives and protect our planet.
In summary, the evolution of monitoring technology is a journey of continuous improvement and adaptation. By leveraging the latest innovations, we can harness the power of data to create safer, more efficient, and sustainable systems for the future. The potential of cutting-edge monitoring equipment is vast, and its impact on our world is only just beginning.